Keep balance is important in daily activities and balance rehabilitation training is essential for maintaining an independent lifestyle in the elderly. Insole X can be used for monitoring the balance ability of the elderly and fall prediction, thus assess the training results and optimize the rehabilitation strategies since diverse balance rehabilitation training equipment has been developed.
Category Uncategorized
GAIT ANALYSIS/ROBOTIC THERAPY |smart insole
The Motion Analysis Laboratory at Spaulding Boston offers both clinical gait evaluations and robotic therapy to assess and treat patients with mobility-limiting conditions including amputation, cerebral palsy, traumatic brain injury, and stroke. During an evaluation, our staff will analyze in detail how you walk using a high-tech multi-camera system. We then develop an individualized treatment plan to correct gait problems. We use advanced robotic technology in rehabilitation sessions, including the Lokomat, a robotic leg exoskeleton which assists patients in re-learning how to walk, and the ARMEO, an arm exoskeleton system that assists patients in improving reaching and grasping movements. Continue reading “GAIT ANALYSIS/ROBOTIC THERAPY |smart insole”
Plantar pressure distribution in patients with neuropathic diabetic foot| smart insole
To describe the plantar pressure distribution in a selected group of patients with diabetic foot and to highlight their alterations in gait cycle, which follow the involvement of the foot in systemic diabetic neuropathy. Methods:Ten patients with diabetic foot due to insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) were studied. Gait cycle kinematics were video-recorded, both in frontal (AP view) and in sagittal (LL view) planes. Plantar pressure measurements+ APview+LLview were synchronized and compared to a computer-graphic generated skeletal model of the foot. Results:In diabetic neuropathic patients, there was a prolonged interval between heel strike and toe-off with respect to normal controls. A limited motion, quite close to frank rigidity, affecting the mid-tarsal, sub-talar and ankle joints was noted. There was an early transfer of load from rear to front-foot. Shear stresses appeared. Metatarsal heads were overloaded both in mag-nitude and in time. Areas of overload present in the static plantar pressure measurement correlated poorly with areas of over-load in dynamic plantar pressure measurement and areas where ulceration was present. Conclusion:Prolonged duration of the gait cycle and shear stresses characterize the plantar pressure pattern of diabetic neuropathic patients. Furthermore, results suggest that static plantar pressure measurement has no clinical correlation with areas where ulcerations are present.
smart shoe lofit samsung

smart shoe smart insole smart
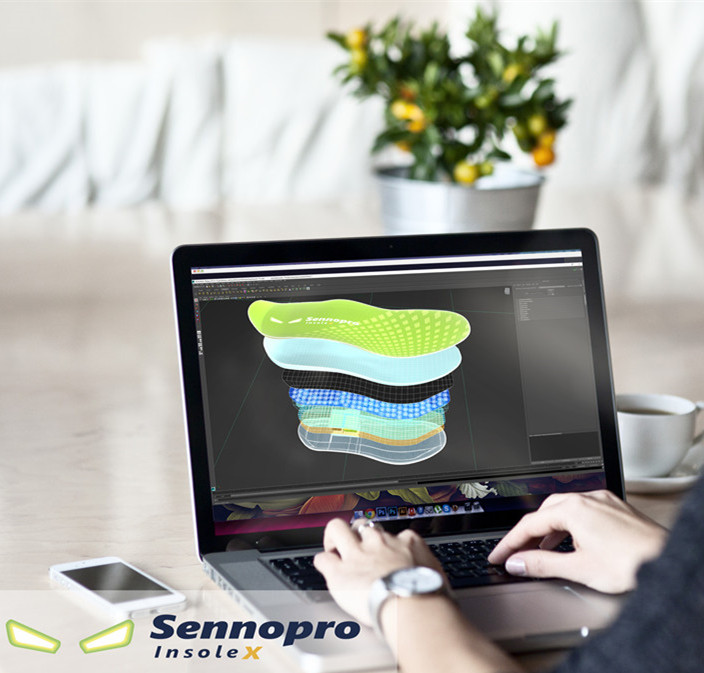

smart insole smart shoes with inertial sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer and pressure sensor)

smart insole smart shoes with inertial sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer and pressure sensor)
running gait analysis wearable technology

running gait analysis
GAIT ANALYSIS WEARABLE TECHNOLOGY

GAIT ANALYSIS
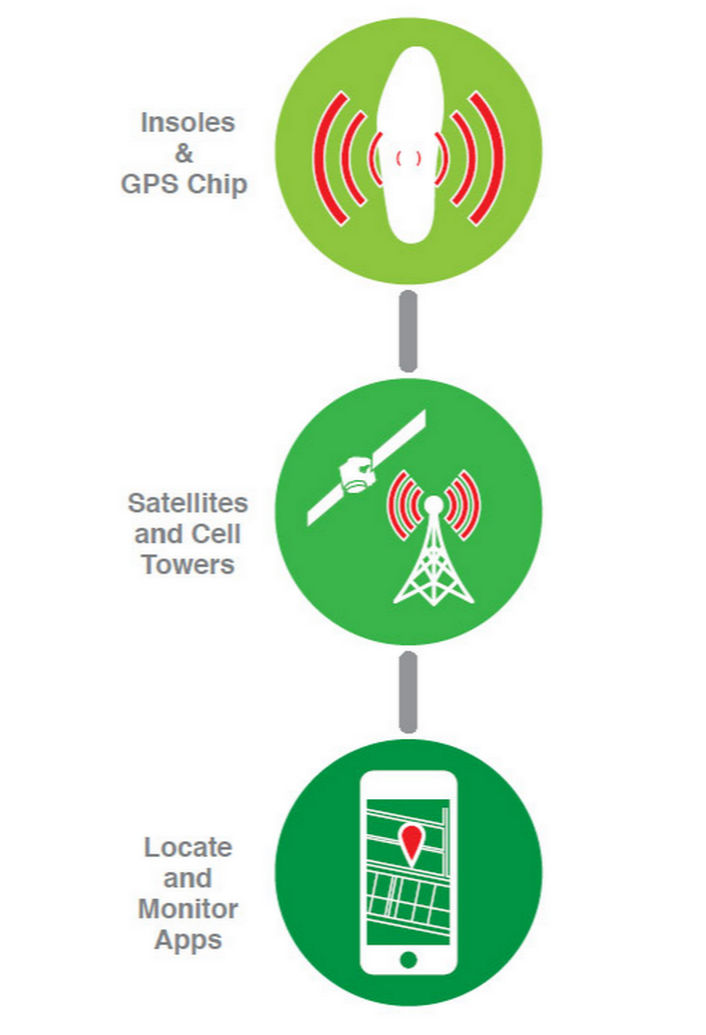
wearable technology smart insole gps
mHealth CES 2016

mHealth CES 2016
